A copper_ silver cell is set up. The copper ion concentration is 0.10 M. The concentration of silver ion is not know.the cell potential when measured was 0.422V determine the concentration of
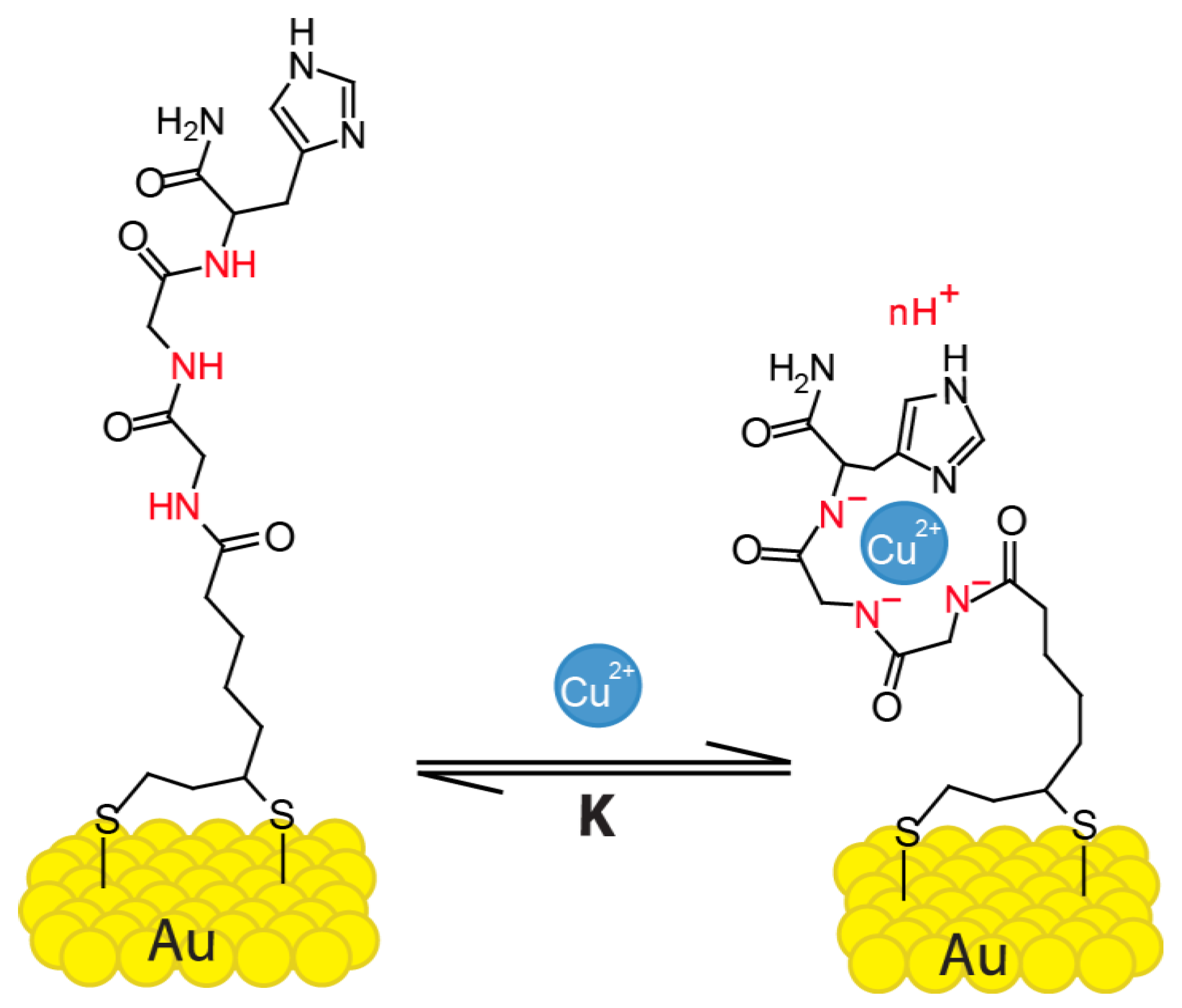
Sensors | Free Full-Text | Detection of Cu2+ Ions with GGH Peptide Realized with Si-Nanoribbon ISFET

Ch 7.1 Forming Ions. Review… Cations are Groups 1A, 2A, and 3A They have positive charges. Anions are Groups 5A, 6A, and 7A They have negative charges. - ppt download

SOLVED: The product solubility constant for copper (I) iodide is 1.1X 10-12 When 0.40 M HCN is added to this ionic salt; forming the complex ion, Cu(CN) 2 with a product formation constant

Colorimetric Detection of Copper(II) Ions Using Schiff‐Base Derivatives - Aydin - 2020 - ChemistrySelect - Wiley Online Library
![In an excess of NH(3(aq.)),Cu^(2+) ion form a deep blue complex ion [Cu (NH(3))(4)]^(2+) having formation constant K(f)=5.6xx10^(11). Calculate the concentration of Cu^(2+) in a solution prepared by adding 5.0xx10^(-3) mole of CuSO(4) In an excess of NH(3(aq.)),Cu^(2+) ion form a deep blue complex ion [Cu (NH(3))(4)]^(2+) having formation constant K(f)=5.6xx10^(11). Calculate the concentration of Cu^(2+) in a solution prepared by adding 5.0xx10^(-3) mole of CuSO(4)](https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/ss/web/355853.jpg)
In an excess of NH(3(aq.)),Cu^(2+) ion form a deep blue complex ion [Cu (NH(3))(4)]^(2+) having formation constant K(f)=5.6xx10^(11). Calculate the concentration of Cu^(2+) in a solution prepared by adding 5.0xx10^(-3) mole of CuSO(4)
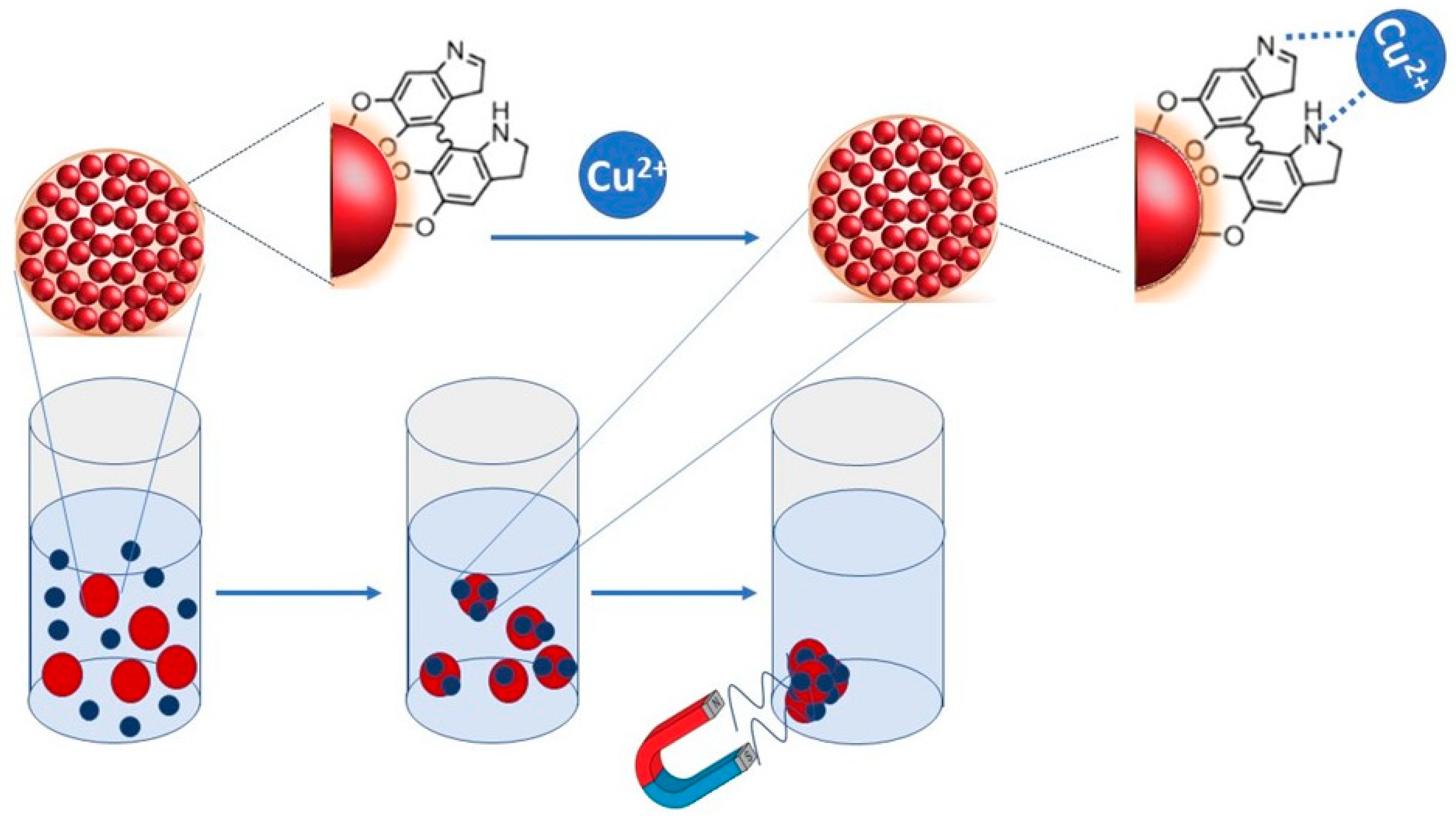
Materials | Free Full-Text | Synthesis and Characterization of SPIONs Encapsulating Polydopamine Nanoparticles and Their Test for Aqueous Cu2+ Ion Removal






.jpg)